On-site utilities
ENGIE, a leading European player
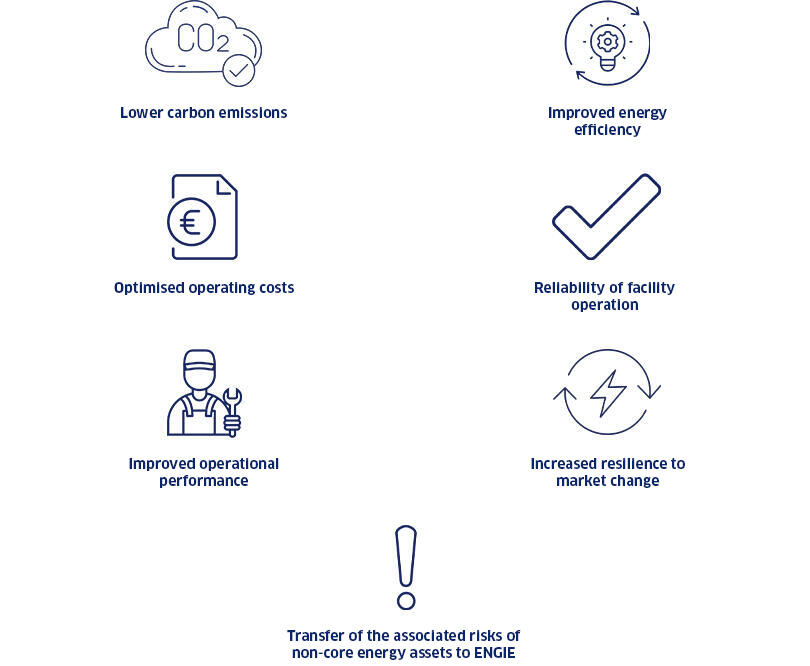
Improving energy usage and operational performance is a key issue for industrial sites manufacturers, as well as public and private buildings operators. To meet such goals, one preferred solution is to manage and optimize on-site utilities. ENGIE is a leader in the sector and provides solutions that use local resources and centralized technologies. These are more efficient, less costly, and generate lower carbon emissions.
How to define on-site utilities?Utilities are produced using energy systems such as boilers, heat pumps, etc. and distributed on client sites in the form of steam, hot water, cooled and/or chilled water, electricity, compressed air, hydrogen, nitrogen, etc. |


To enable its industrial customers to remain focused on their core activities, ENGIE manages the whole energy services value chain, from design, finance, and construction, to operation, maintenance, and supply of the utility. In this way, the Group covers the risks related to the utilities and is committed to their economic performance, availability, and long-term quality. Alongside its industrial customers, ENGIE also proposes solutions for owners of public or private buildings.
Local and renewables solutions
On-site utilities take advantage of either available, local energy resources or of the most suitable renewable technologies such as:
- Waste heat, which consists in recovering energy lost during industrial processes, potentially in association with heat pumps.
- Biomass or biogas boilers, which produce heat energy using local sources of supply.
- Cogeneration, which uses biomass and biogas to produce heat and electricity.
- Trigeneration which goes further by producing cooling in parallel to heat and electricity.
- Methanization, or the transformation of biowaste into biogas to supply boilers and/or co-generation or tri-generation systems.
- Solar thermal, which transforms the radiation of the sun into heat for a factory, for example.
- Geothermal energy, which harness natural heat from the ground and delivers it for industrial use, potentially in association with heat pumps.
- Green hydrogen, produced on or off-site and which replaces carbon-rich hydrogen in industrial processes.
Furthermore, ENGIE offers energy efficiency measures for the utilities it delivers, in particular through Energy Performance Contracts.
